Aircraft Engine Maintenance and Its Critical Role in Aviation Safety
Aircraft engine maintenance is one of the most essential aspects of aviation safety. The aircraft engine is the heart of every airplane, providing the necessary power for takeoff, flight, and landing. It is a complex system made up of compressors, turbines, and combustion chambers that must operate together in perfect harmony to guarantee safe and efficient performance.
Any malfunction within an aircraft engine can lead to serious consequences, including power loss, reduced control, or in the worst case, a crash. That’s why regular aircraft engine maintenance is crucial — it ensures the reliability, safety, and longevity of every flight operation.
Preventive maintenance forms the foundation of safe aviation. It focuses on early detection of potential issues, through scheduled inspections, overhauls, and component replacements before small problems turn into major failures. Airlines that consistently invest in preventive maintenance not only avoid catastrophic incidents but also save on expensive repairs and reduce downtime.
Technology has transformed how aircraft engine maintenance is carried out. Predictive systems powered by data analytics and machine learning now detect early warning signs of component wear or performance degradation. These innovations allow engineers to act before failures occur, increasing aircraft reliability and reducing maintenance costs.
Digital Twin Technology takes this transformation even further. By creating a virtual replica of an aircraft engine, it allows maintenance specialists to monitor performance in real time, simulate different flight conditions, and predict future behavior. This proactive approach enhances operational efficiency, reduces fuel consumption, and improves overall flight safety.
The Human Factor in Aircraft Engine Maintenance
While technology continues to evolve, human expertise remains at the core of safe aircraft engine maintenance. Understanding the human factor — how fatigue, workload, and communication affect maintenance quality — is critical for preventing errors. Training, clear procedures, and ergonomic tool design all contribute to safer maintenance environments.
Maintenance technicians play a decisive role in ensuring engine airworthiness. Well-structured schedules, accurate labelling, and intuitive tools reduce the chance of mistakes and improve efficiency. Communication across all levels of maintenance teams and with aviation authorities also strengthens safety culture and minimizes human error.
Knowledge of human performance helps maintenance organizations identify and mitigate risks before they impact aircraft reliability. By integrating human factors principles with modern technologies like digital twin systems and predictive maintenance software, airlines can achieve the highest standards of reliability and safety in aviation today.
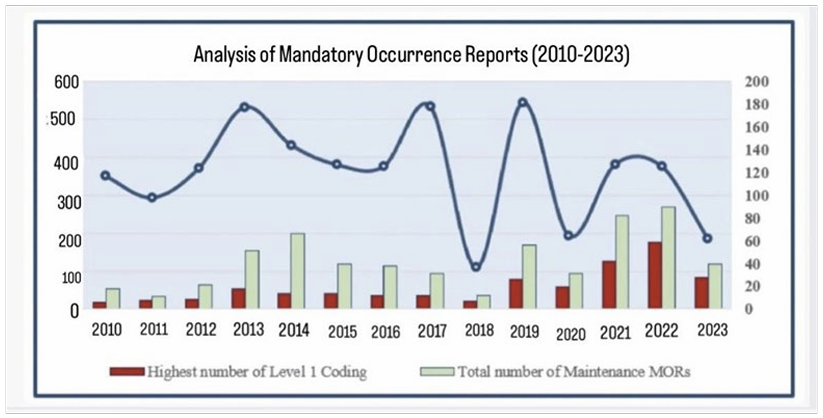
Figure 1: Analysis of Mandatory Reports
The chart below illustrates the trend in Mandatory Occurrence Reports (MORs) related to aircraft engine maintenance between 2010 and 2023. It highlights two main factors: the total number of maintenance-related MORs and the highest annual count of Level 1 coding incidents.
Over the years, the total number of MORs has fluctuated, with the lowest activity recorded in 2018. In recent years, however, maintenance-related occurrences have shown a noticeable increase, now representing more than 40 percent of all MORs. Peaks in Level 1 coding incidents were recorded in 2013, with 18 incidents, and again in 2020, when the number rose to 26.
These statistics reflect the growing complexity of modern aircraft engine maintenance and emphasize the importance of preventive measures, predictive analysis, and improved maintenance planning supported by new technologies.
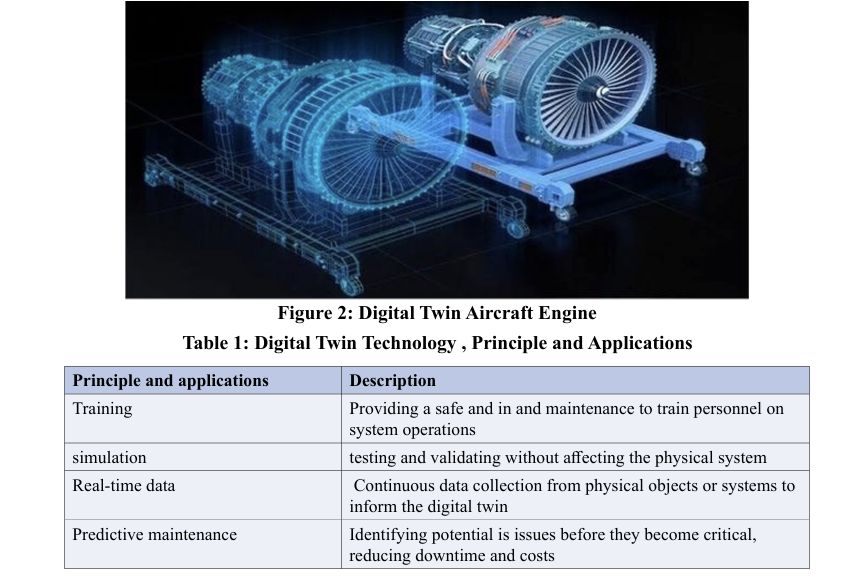
Digital Twin Technology in Aircraft Engines
Digital twin technology represents one of the most transformative innovations in the field of aircraft engine maintenance. It allows engineers to create a virtual model—or “twin”—of a real engine, replicating every structural component, system, and operational behavior. This digital counterpart mirrors the physical engine in real time through a network of sensors that continuously collect data on temperature, pressure, vibration, fuel flow, and other performance metrics.
The data is transmitted to the digital twin, where advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms process it to monitor the engine’s health and predict potential malfunctions. The system can identify abnormal patterns or deviations from standard performance long before they become critical, enabling maintenance teams to take preventive action instead of reacting after a failure occurs.
Beyond real-time monitoring, digital twin technology allows for the simulation of various operational scenarios and “what-if” analyses. Engineers can test maintenance strategies, evaluate upgrades, and optimize performance without physically touching the engine. This virtual testing capability significantly improves reliability and reduces the cost of experimental trials.
Creating a digital twin involves combining data-driven models, complex simulations, and live operational data. Inputs come from multiple sources — engine sensors, flight data recorders, and historical maintenance logs — which are integrated into a comprehensive digital environment. Software platforms play a crucial role by managing and analyzing the vast amounts of information required to maintain an accurate and constantly updated model.
The benefits of implementing digital twin technology in aircraft engines are substantial. Airlines and manufacturers report greater maintenance efficiency, fewer unscheduled repairs, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety. Real-time insights enable teams to detect potential failures early, optimize engine performance, and even improve fuel efficiency while lowering emissions.
Several major manufacturers already rely on this technology. Rolls-Royce, for instance, uses digital twins to oversee its Trent XWB engines that power the Airbus A350 XWB. Through continuous monitoring and predictive analytics, the company has reduced engine downtime, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced overall engine reliability.
However, the adoption of digital twin technology in aviation is not without challenges. Data privacy, cybersecurity, and the lack of standardized data formats remain ongoing issues. Despite these hurdles, the potential of digital twins to revolutionize aircraft engine maintenance is undeniable, marking a new era of smart, predictive, and efficient aviation management.
Case Study on Aircraft Engine Maintenance and Flight Safety
Real-world examples clearly demonstrate how aircraft engine maintenance directly affects flight safety. Proper maintenance, inspection, and predictive monitoring have proven to prevent failures that could otherwise lead to catastrophic consequences.
One of the most notable incidents occurred in 2010, when a Qantas Airways Airbus A380 experienced an uncontained engine failure shortly after takeoff. Debris from the failed engine struck the wing and damaged the aircraft’s fuel tanks. Despite the severity of the situation, the crew successfully returned the aircraft for a safe landing — a result of both the engine’s redundancy and the pilots’ exceptional training. This event reinforced the critical importance of routine aircraft engine maintenance and highlighted why airlines must continue investing in advanced predictive maintenance systems.
Another case occurred in 2018, involving a Southwest Airlines Boeing 737 that suffered an engine failure during flight, tragically resulting in the death of a passenger. Investigators attributed the failure to metal fatigue in one of the engine’s fan blades — an issue that could likely have been identified through regular inspection and timely maintenance procedures.
These examples underline the vital role of preventive and predictive aircraft engine maintenance in modern aviation. Routine inspections, component monitoring, and the use of emerging technologies such as digital twin models can significantly reduce risks and enhance overall aviation safety. Each lesson learned from these incidents has contributed to stronger maintenance protocols, better training, and more advanced tools for detecting early signs of engine fatigue and wear.

Digital Twin Technology in Aircraft Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul
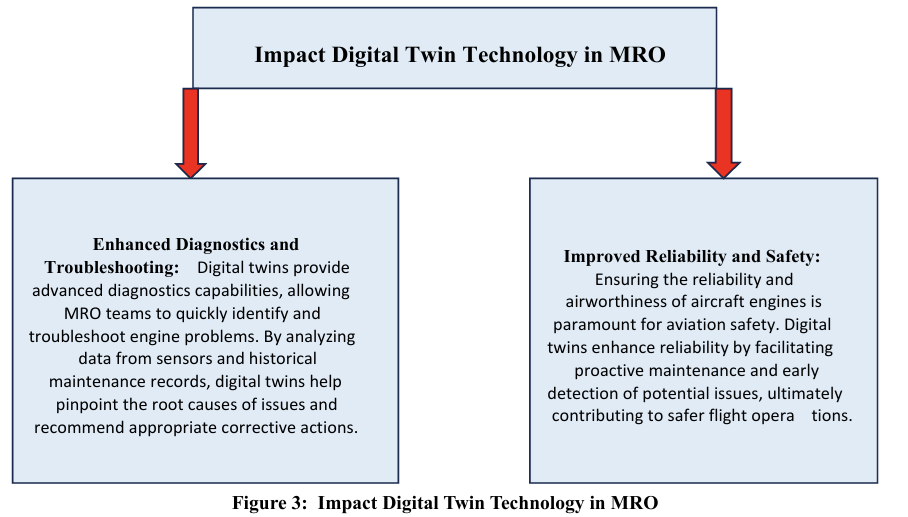
Digital twin technology is transforming the way maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) operations are performed in modern aviation. By creating a precise virtual replica of an engine or system, maintenance teams can continuously monitor an aircraft’s health, predict potential failures, and plan interventions before issues become critical.
In the context of aircraft engine maintenance, digital twins provide real-time insight into every parameter that affects engine performance — from temperature and vibration to fuel efficiency and wear trends. This data-driven approach allows technicians to evaluate the engine’s current condition, predict its future state, and schedule maintenance activities proactively. The result is improved reliability, reduced unplanned downtime, and significant cost savings across the MRO process.
Through digital twin technology, maintenance teams can simulate different operational scenarios, test various repair strategies, and optimize workflow planning. The ability to forecast when and where maintenance will be needed helps avoid unnecessary ground time, ensuring that aircraft remain operational for longer periods.
Beyond efficiency, digital twins contribute directly to aviation safety. Predictive analytics derived from live data allows for early detection of anomalies and component fatigue, minimizing the likelihood of in-flight failures. As a result, aircraft maintenance transitions from reactive to proactive — preventing problems before they impact performance.
Ultimately, integrating digital twin technology into MRO operations represents a shift toward smarter, more connected aviation maintenance. By combining real-time monitoring, predictive insights, and automated data analysis, digital twins empower technicians to keep engines in optimal condition, ensuring higher reliability, lower operational costs, and safer skies.
Conclusion
Aircraft engine maintenance remains one of the most critical pillars of aviation safety. Regular inspections, timely repairs, and thorough overhauls ensure that engines operate at peak performance and that any potential issues are detected before they escalate. Preventive maintenance programs not only protect passengers and crew but also extend engine lifespan and optimize airline operating costs.
The integration of advanced technologies — particularly predictive maintenance and digital twin technology — is redefining how the aviation industry approaches reliability. Through real-time monitoring and intelligent data analysis, maintenance teams can anticipate failures, enhance performance, and minimize downtime. As these innovations mature, they promise a future where safety, efficiency, and sustainability coexist seamlessly.
Despite challenges such as data standardization and system integration, the continuous evolution of digital twin technology is transforming aircraft engine maintenance into a proactive, data-driven discipline. Airlines that adopt these solutions today are building the foundation for a safer and more efficient tomorrow.
To explore how modern twin-engine aircraft integrate such advanced systems for reliability and control, read also:
8 Common Systems You’ll Find On Twin Engine Aircraft
